Monitoring the Respiratory System using Regional Impedance Analysis
Seiten
Pathologies of the respiratory system are potentially life-threatening, especially in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit. When not diagnosed and treated in an early stage, they can develop into acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which is a critical condition with high mortality. Unfortunately, current medical diagnostic methods are not available continuously at the bedside. Continuous monitoring, however, could significantly improve the outcome of the patient.
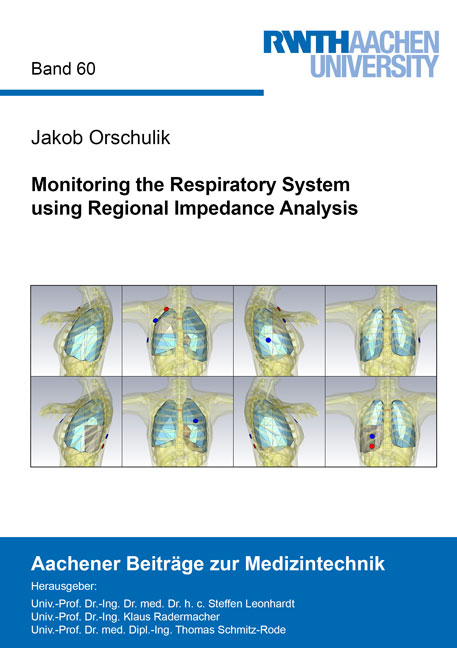
This thesis investigates the potential of bioimpedance measurements to monitor the respiratory system. Based on theoretical considerations, criteria are developed that quantify the ability of specific tetrapolar electrode configurations to focus impedance measurements on lung regions of interest (ROI). From this, adjusted electrode positions are determined in simulations that amplify changes inside the ROI. General guidelines on electrode placement are derived that could be transferred into clinical practice.
These guidelines are tested by evaluating if pathological changes in specific ROIs are detectable. For this, ex-vivo validation studies in simulations and a phantom experiment are performed. The results in both studies confirms the benefit of adjusted electrode positions. The validity of the concept is further validated in an in-vivo animal trial in 17 female pigs, split into three groups. In two groups, ARDS is established using different methods, while one group serves as the control group. Impedance features are extracted and examined in statistical analysis. It is shown that the distributions of extracted features are significantly different between the three groups. Hence, the results indicate that regional impedance analysis is a promising tool to monitor the respiratory system.
This thesis investigates the potential of bioimpedance measurements to monitor the respiratory system. Based on theoretical considerations, criteria are developed that quantify the ability of specific tetrapolar electrode configurations to focus impedance measurements on lung regions of interest (ROI). From this, adjusted electrode positions are determined in simulations that amplify changes inside the ROI. General guidelines on electrode placement are derived that could be transferred into clinical practice.
These guidelines are tested by evaluating if pathological changes in specific ROIs are detectable. For this, ex-vivo validation studies in simulations and a phantom experiment are performed. The results in both studies confirms the benefit of adjusted electrode positions. The validity of the concept is further validated in an in-vivo animal trial in 17 female pigs, split into three groups. In two groups, ARDS is established using different methods, while one group serves as the control group. Impedance features are extracted and examined in statistical analysis. It is shown that the distributions of extracted features are significantly different between the three groups. Hence, the results indicate that regional impedance analysis is a promising tool to monitor the respiratory system.
| Erscheinungsdatum | 24.11.2020 |
|---|---|
| Reihe/Serie | Aachener Beiträge zur Medizintechnik ; 60 |
| Verlagsort | Düren |
| Sprache | englisch |
| Maße | 148 x 210 mm |
| Gewicht | 260 g |
| Themenwelt | Medizin / Pharmazie |
| Technik ► Medizintechnik | |
| Schlagworte | Bioimpedance • Bioimpedance Analysis • Bioimpedance Spectroscopy • Respiratory System |
| ISBN-10 | 3-8440-7687-5 / 3844076875 |
| ISBN-13 | 978-3-8440-7687-5 / 9783844076875 |
| Zustand | Neuware |
| Haben Sie eine Frage zum Produkt? |
Mehr entdecken
aus dem Bereich
aus dem Bereich
Schulungs- und Fortbildungsnachweis zur Dokumentation von …
Buch | Softcover (2024)
TÜV Media GmbH TÜV Rheinland Group (Verlag)
6,53 €
Moderne Verfahren in Diagnostik und Therapie
Buch (2023)
Spektrum der Wissenschaft (Verlag)
9,30 €
Buch | Softcover (2023)
De Gruyter (Verlag)
94,95 €